(Everydayhealth, 2020)
Medically reviewed by Dr. Riaz Ali Shah.
When you talk about tuberculosis today with people in developed countries, they are frequently astonished by its existence as it is believed to be an illness that is extinct. And, while tuberculosis is an ancient disease, it remains a very contemporary concern.
Although tuberculosis’s causative microorganisms were discovered only 140 years ago, the disease has existed for thousands of years. By 2020, it caused around 10 million illnesses and 1.5 million fatalities. Despite these unacceptably high rates, the disease is curable, and in nations with sufficient resources, tuberculosis prevention is possible. It can be not only cured but also discovered in time to prevent community transmission.
What is Tuberculosis?
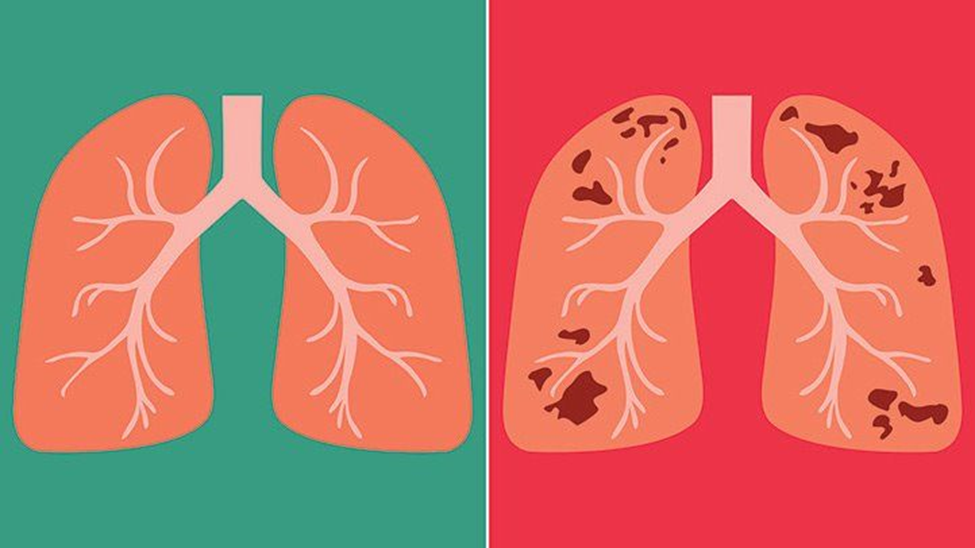
Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection that most commonly affects the lungs. However, it can also affect the neurological system, bones, glands, and abdomen. Tuberculosis is one of the top ten causes of death worldwide, with millions contracting the disease each year.
Although tuberculosis is a dangerous disease, it is treatable and curable with medications in the correct circumstances. Despite this, recent investigations have discovered the emergence of a drug-resistant form of tuberculosis, which is primarily found in developing nations. Unfortunately, the majority of tuberculosis patients in impoverished countries lack access to the necessary healthcare to prevent and treat infection spread.
(Everydayhealth, 2020)
How is Tuberculosis Spread?
While it is well accepted that tuberculosis is an infectious disease, how does one contract tuberculosis? Tuberculosis is an airborne infection, which means that it is spread through spitting, sneezing, and coughing. This makes tuberculosis extremely contagious because it does not require direct touch with an infected individual but rather proximity to their breathing space.
What are tuberculosis causes and risk factors?
Tuberculosis risk factors include anything that impairs a person’s immune system or puts them in close contact with someone who has active tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis is a bacterial ailment that spreads through contact with an infected person. In most cases, persons in good health are able to eliminate the bacteria on their own. When the body’s natural defenses are unable to eliminate the bacteria, they normally prevent them from spreading throughout the body.
In some cases, the germs will persist in the body even if one does not exhibit symptoms; this is referred to as latent tuberculosis, in which one is not contagious to others. If, on the other hand, the immune system is unable to limit or eliminate the infection, it can spread throughout the body. Once this occurs, symptoms will manifest within weeks or months. This is referred to as active tuberculosis because it indicates that the sick individual is now contagious to others.
Some common risk factors include:
- Substance Abuse and drinking: damage the immune system
- Autoimmune illnesses: taking Medication That Weakens the Immune System
- Kidney Disease and Diabetes Chronic illnesses: impair the immune system, making it difficult for the body to fight TB
- Organ Transplants: the medications people take to avoid the rejection of an organ transplant can weaken the immune system
- Cancer Chemotherapy: impairs the immune system
What is the first sign of tuberculosis?
Some common tuberculosis symptoms include:
- Neck swellings
- Appetite loss
- Fatigue and fatigue
- High temperature
- Night sweats
- Weight loss
- A persistent cough lasting more than three weeks, bringing up mucus and blood

(WHO, 2020)
Tuberculosis treatment and prevention
To begin, a tuberculosis vaccine, the BCG vaccine, can be administered to infants, children, and adults under the age of 35 in countries. Despite this, vaccination is not frequently delivered in the regions because healthcare institutions are underfunded and overburdened.
Similarly, tuberculosis can almost always be cured in developing nations with a six-month course of antibiotics. Even if one has a drug-resistant type of tuberculosis, one may be able to fight it off with six or more treatments.
If one comes into intimate contact with someone who has tuberculosis, they may be tested to ensure that they are not also affected. Tuberculosis test include skin testing, tuberculosis blood test, and chest X-rays.
By: Sanya Zahid
Citations:
https://www.everydayhealth.com/tuberculosis/guide/
https://www.everydayhealth.com/tuberculosis/guide/latent/
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/8856
https://www.who.int/campaigns/world-tb-day/2020/campaign-materials






