Medically reviewed by Dr. Sumbul Wahab.
What is Cervical Cancer?
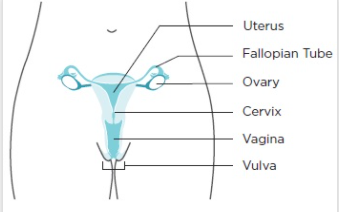
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer where the cells change in a women’s cervix. Cervix connects the vagina and uterus. The vagina is a birth canal and the uterus is a womb, where babies grow.
Cervical Cancer affects the deeper tissues in the cervix, where cells grow out of control and can spread cancer to other parts of the body, mostly: the liver, lungs, rectum, and vagina.
Women aged between 35-44 years old are more likely to contract it.
However, more than 15% of new instances occur in women over the age of 65, particularly those who haven’t been undergoing regular tests.
Cervical Cancer symptoms and signs
-
- Blood spots or light bleeding during or after periods.
-
- Heavier than usual menstrual bleeding.
-
- Bleeding after pelvic examination and intercourse.
-
- Pain during sexual intercourse
-
- Heavy vaginal discharge
-
- Bleeding after menopause and consistent unexplained pelvic pain.
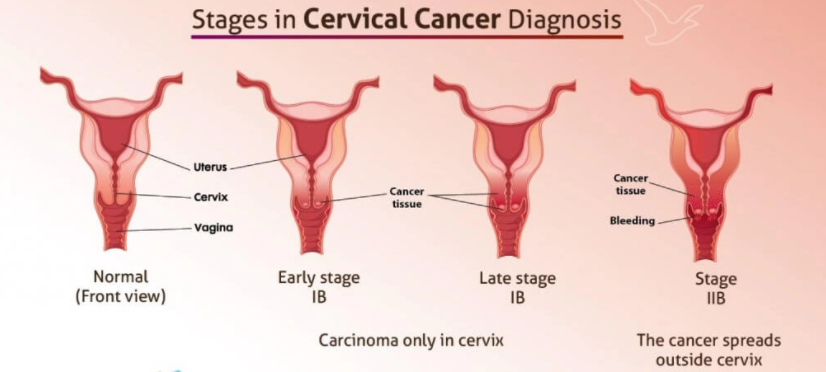
Cervical Cancer stages
According to FIGO, the following are the cervical cancer stages:
Stage I
At this stage, cervical cancer has spread to the deeper lining of the cervix and uterus, but not to other parts of the body.
Stage II
At this stage, cancer has spread to other nearby areas of the vagina or tissue near the cervix but is within the pelvic region.
Stage III
At this stage tumor has spread to the pelvic wall, impairing kidney function and lymph nodes are swollen.
Stage IVA
Cancer has spread to the bladder and rectum.
Stage IVB
Cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Cervical Cancer Treatment.
Depending upon the stage and the kind of cervical cancer, the following are the most common types of cervical cancer treatment:
Surgery
Cancer tissue is operated on and surgically removed by the doctor
Chemotherapy
Using specific medicines to shrink or kill cancer cells.
Radiation
Using high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells.
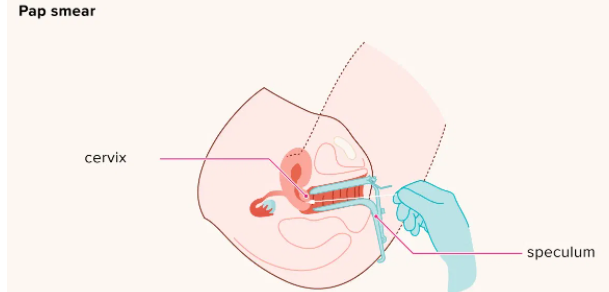
Cervical Cancer screening test
The primary preventative intervention used to lower the burden of cervical cancer is screening. The primary goal of cervical cancer screening is to detect early-stage of cancer.
This is usually done through Pap smear-based screening, in which cells are gently scraped off from the cervix and sent for examination regarding abnormal growth.
CITATIONS:
https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/cervical/basic_info/index.htm
https://www.webmd.com/cancer/cervical-cancer/cervical-cancer
https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/cervical-cancer/symptoms-and-signs
https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/cervical-cancer/stages
https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/s12889-018-5023-7.pdf
https://www.healthline.com/health/pap-smear-pap-test-what-to-expect




